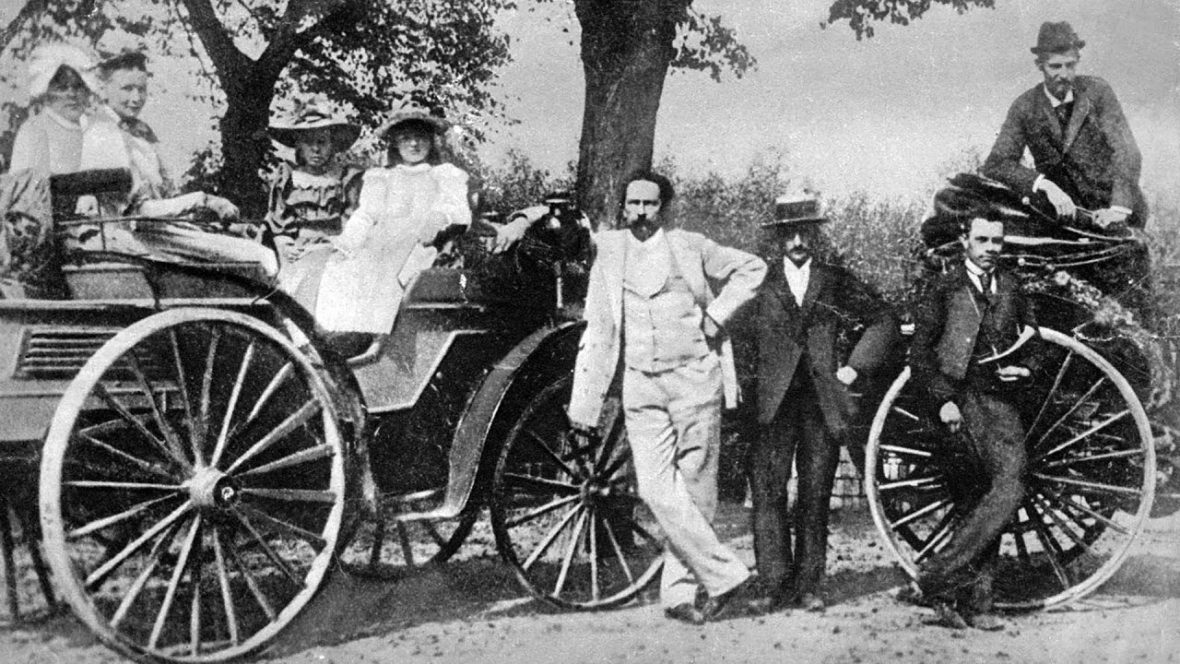
Karl Friedrich Benz was a German engine designer and automobile engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical automobile. He received a patent for the motorcar on January 29, 1886. Take a look below for 28 more fascinating and interesting facts about Karl Benz.
1. Benz was born Karl Friedrich Michael Vaillant, on November 25, 1844, in Muhlburg, now a borough of Karlsruhe, Baden-Wurttemberg, which is part of modern Germany.
2. His mother was Josephine Vaillant and his father was Johann Georg Benz, a locomotive driver, whom his mother married a few months after giving birth to Karl.
3. According to German law, the child acquired the name “Benz” by legal marriage of his parents Benz and Vaillant.
4. When he was two years old, his father died of pneumonia, and his name was changed to Karl Friedrich Benz in remembrance of his father.

5. Despite living in near poverty, his mother strove to give him a good education.
6. Benz attended the local Grammar School in Karlsruhe and was a prodigious student.
7. In 1853, at the age of nine, he started at the scientifically oriented Lyceum. Next, he studied at the Poly-Technical University under the instruction of Ferdinand Redtenbacher.
8. Benz had originally focused his studies on locksmithing, but he eventually followed his father’s steps toward locomotive engineering.
9. On September 30, 1860, at the age of 15, he passed the entrance exam for mechanical engineering at the University of Karlsruhe, which he subsequently attended. He graduated on July 9, 1864, at the age of 19.
10. During his early adulthood, while riding his bicycle, Benz started to envision concepts for a vehicle that would eventually become the horseless carriage.

11. Following his formal education, Benz had seven years of professional training in several companies, but didn’t fit well in any of them.
12. His training started in Karlsruhe with two years of varied jobs in a mechanical engineering company.
13. After Karlsruhe, he moved to Mannheim to work as a draftsman and designer in a scales factory.
14. In 1868, he went to Pforzheim to work for a bridge building company Gebruder Benckiser Eisenwerke und Maschinenfabrik.
15. Finally, he went to Vienna for a short period to work at an iron construction company.
16. In the 1870s, Benz established a metal working factory in Mannheim, Germany. He began to build different parts for an engine driven vehicle, and the world’s first car was built in 1885.
17. Benz’s first car was called the Benz Patent Motorwagen. The motorized tricycle had no gears, and was difficult to control, crashing into a wall while being demonstrated.

18. His wife secretly tested the new car by driving it a distance of 106 kilometers to her mother’s house. Today, every two years, an antique car race is held along that same stretch of road.
19. In 1894, Benz made the Velo, the world’s first production car. It took part in the world’s first car race in France, with an average speed of just over 12 kilometers per hour.
20. Benz designed the world’s first lorry in 1895. A year later, he introduced a revolutionary flat engine design, a design that is still used by car manufacturers such as Porsche.
21. By the 1920s, the Benz car company was competing with its biggest rival, Daimler.
22. The Great Depression led to the two companies merging into one company called Daimler-Benz.
23. In 1914, during his 70th birthday, Benz was awarded an honorary doctorate by his alma mater, the Karlsruhe University.

24. Benz died at home in Ladenburg, on April 4, 1929, at the age of 84 from pneumonia.
25. Bertha Benz remained in their family villa and was honored with the title “Honorable Senator,” by the Technical University of Karlsruhe in 1944.
26. On May 5, 1944, Bertha, at the age of 95, died at the family villa.
27. The Benz family villa is now designated as a historic site and is utilized as a scientific meeting facility.
28. The nonprofit corporation, the Gottlieb Daimler and Karl Benz Foundation, own the Benz villa that honors both Bertha and Karl Benz for their roles in the history of automobiles.